
The cost of business assets can be expensed each year over the life of the asset to accurately reflect its use. The expense amounts can then be used as a tax deduction, reducing the tax liability of the business. There are several steps to follow when calculating amortization for intangible assets. Since intangible assets are not easily liquidated, they usually cannot be used as collateral on a loan. Understanding amortized Cost helps you evaluate the actual value of investments over time.

Identify the cost of the intangible asset

Another difference is that the IRS indicates most intangible assets have a useful life of 15 years. For example, computer equipment can depreciate quickly because of rapid advancements in technology. A company spends https://www.bookstime.com/articles/completed-contract-method $50,000 to purchase a software license, which will be amortized over a five-year period.
Understanding Amortization

As premiums are gradually amortized, it affects how interest income from these bonds is recognized over time. Initially, when a bond is purchased at a premium, only part of each interest payment represents actual interest income. As amortization progresses, a more significant amount of each payment becomes recognized as interest income until all premiums have been fully amortized.
- Depletion refers to the allocation of the cost of natural resources, whereas amortization refers to intangible assets.
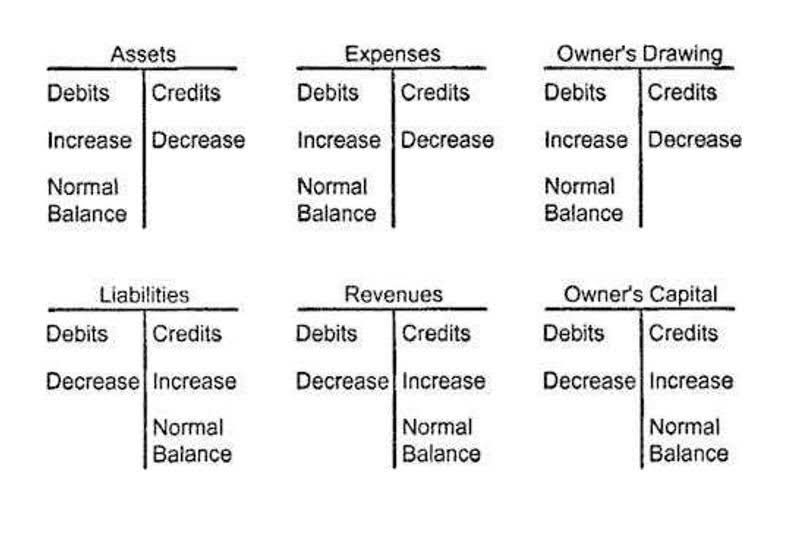
- You must use depreciation to allocate the cost of tangible items over time.
- In addition, depreciation is recorded for those items included in the plant and equipment account, even if they are temporarily not in use.
- It used to be amortized over time but now must be reviewed annually for any potential adjustments.
- The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice.
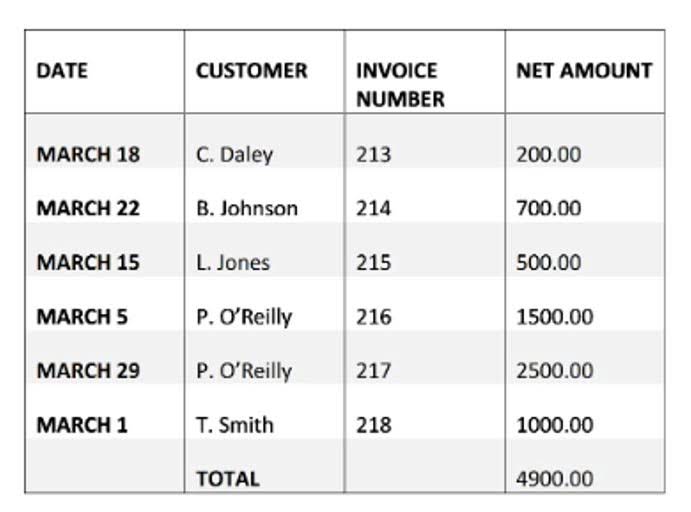
Example of Amortization vs. Depreciation
A percentage of the purchase price is deducted over the course of the asset’s useful life. If you’re a real estate or REIT investor, knowing that loans typically don’t start paying off much of the principal on real estate right away may help you better understand the strategy of a REIT. Patriot’s online accounting software is easy-to-use and made for https://www.instagram.com/bookstime_inc small business owners and their accountants. Suppose a company, Dreamzone Ltd., purchased a patent for $100,000 with a useful life of 10 years. Dreamzone divided the purchase price by the useful life to amortize the patent’s cost. Turn to Thomson Reuters to get expert guidance on amortization and other cost recovery issues so your firm can serve business clients more efficiently and with ease of mind.
- An amortization schedule is used to reduce the current balance on a loan—for example, a mortgage or a car loan—through installment payments.
- In the amortization of loans, you’ll generally have a payment that’s fixed, with interest and principal payments that change over time.
- Amortization is when an asset or a long-term liability’s value or cost is gradually spread out or allocated over a specific period.
- Amortization will, however, begin when it is determined that the useful life is no longer indefinite.
- Depletion is another way in which the cost of business assets can be established in certain cases but it’s relevant only to the valuation of natural resources.
Amortizing an Intangible Asset
For information pertaining to the registration status of amortization refers to the allocation of the cost of 11 Financial, please contact the state securities regulators for those states in which 11 Financial maintains a registration filing. When a legal life does not exist, as for goodwill, the selection of service life is potentially more flexible.
Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
Some assets subject to amortized Cost include bonds held until maturity, loans receivable, intangible assets like patents or copyrights, and certain long-term investments. In conclusion, understanding the concept of amortized Cost is crucial in various financial aspects. It allows businesses to accurately account for assets and liabilities over time, ensuring transparency and compliance with accounting standards. Organizations can effectively manage their investments and optimize returns by calculating premium amortization for bonds sold before maturity. Amortization plays a crucial role in accounting by helping to match expenses with revenues over time.